Olive oil
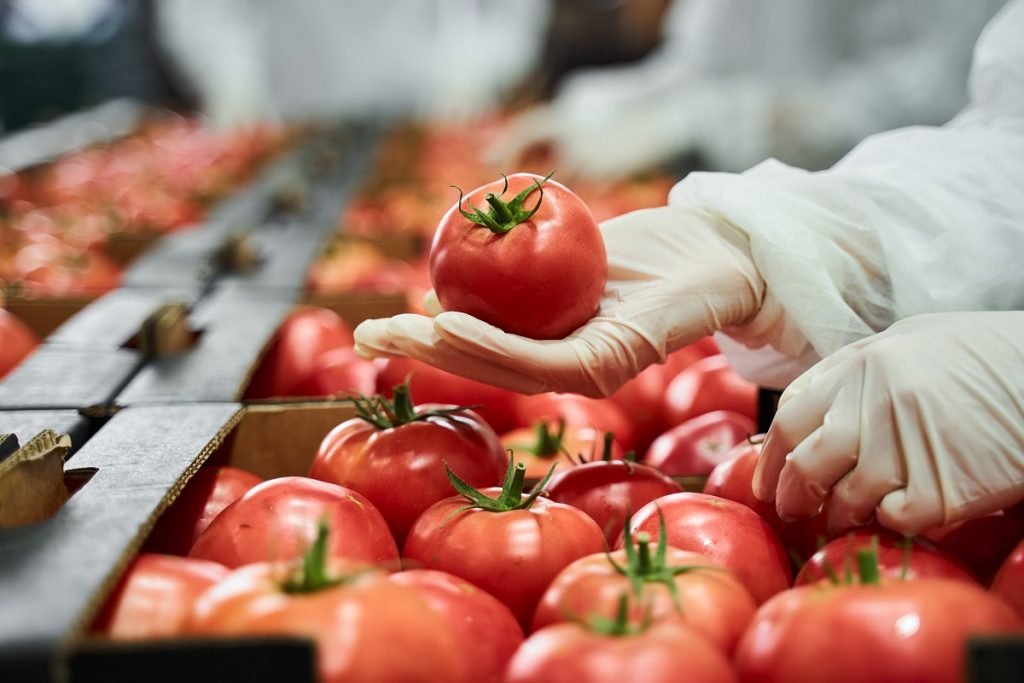



The accredited Microbiological & Chemical Laboratories VIOCHIMIKI offer you laboratory support in any analysis you will need from production to the standardization of olive oil.
Chemical Analysis of Olive Oil and Vegetable Oils
* Acidity level
*Peroxide number
*Κ232
*K268
*DK
Organoleptic evaluation
Polyphenols
Fatty acid profiles
Waxes
Pesticide residue detection
Plasticisers – Phthalates
Benzo[a]pyrene and PAHs
Nutrition labelling under Kan. 1169/2011
Analysis of oil content in oleopyrene
*Accredited tests according to ISO 17025, No. 689 ESYD
Interpretation of parameters
Depending on its qualitative characteristics, olive oil is classified in a corresponding category (extra virgin, virgin, virgin olive oil, nuclear oil, etc.). In the case of standardisation, the category to which the olive oil belongs must be indicated.
The basic categorisation is carried out by determining the parameters of Acidity, Peroxide Number and Absorption in the ultraviolet.
What do each of these parameters mean for the quality of olive oil?
A) Degree of acidity
This refers to the free fatty acid content expressed as % oleic acid. A high acidity value means that the olive oil has been affected by fruit diseases, hydrolysis or oxidation.
B) Peroxide number
Peroxides are chemical compounds formed mainly by the reaction of oxygen with olive oil. The concentration of peroxides is an indicator of the initial stage of oxidation (rancidity) of the olive oil. A high peroxide value means that the olive oil has undergone oxidative deterioration and will have little resistance to time.
C) Absorption in the ultraviolet
This refers to the indicators K232, K268 and DK. It determines the absorption of radiation in the ultraviolet spectrum (wavelengths 232 nm and 268 nm). UV absorption is based on the fact that primary oxidation products absorb at 232 nm, while secondary products absorb at 268 nm.
K232: Index of initial or intermediate oxidation state. A high value indicates a long storage time of the oil or a long time of the fruit before pressing.
C268: Indicator of advanced oxidation or refining stage. A high value indicates old harvest olive oil or olive oil adulterated with another refined or old oil.
DK: Mathematical relationship between the previous two coefficients. It is a criterion for distinguishing a poor quality olive oil from an olive oil which has been adulterated with another refined oil.
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2022/2104 concerning the marketing standards for olive oil
Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/2105 laying down rules on conformity checks on marketing standards for olive oil and methods of analysis of the characteristics of olive oil
Regulation (EU) 1308/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council establishing a common organisation of agricultural markets (Descriptions and definitions of olive oils and olive-pomace oils)
Regulation (EU) 2018/1096 on the labelling of standardised olive oil
